With 3.2 divorces per 1,000 inhabitants in 2022, Alabama maintains one of the highest divorce rates in the nation, affecting thousands of families across the state each year.
Recent legislative developments in Alabama are reshaping how courts determine child support obligations and custody arrangements, potentially affecting the financial security and living arrangements of children throughout the state.
These new Alabama child support laws reflect evolving perspectives on parental responsibilities and children’s financial needs from conception through adulthood.
Understanding Current Child Support Guidelines in Alabama
Alabama employs the Income Shares Model to calculate child support obligations, establishing payment amounts based on both parents’ combined gross income and the proportional financial responsibility each parent would typically provide in an intact household.
The state’s child support guidelines, formally known as Rule 32 of the Alabama Rules of Judicial Administration, underwent significant amendments effective June 1, 2023. Key components of the current system include:
- Basic support calculations: Courts determine obligations using standardized forms (CS-42 or CS-42-S) that consider both parents’ monthly gross income.
- Healthcare coverage costs: The pro-rata portion of health insurance premiums attributable to children must be calculated and included in support obligations.
- Income withholding requirements: Employers must automatically deduct support payments from the obligor’s paycheck and submit them to the Alabama Child Support Central Payment Center.
- Mandatory documentation: All parties must file a Child-Support-Obligation Income Statement/Affidavit (Form CS-41) in proceedings to establish or modify support.
The Alabama Central Disbursement Division (ACDD) processes all payments, while the Child Support Enforcement Program (CSE) handles enforcement for accounts falling into arrears, ensuring consistent collection and distribution of support funds throughout the state.
Senate Bill 18: Retroactive Pregnancy Support
The Alabama Senate unanimously passed Senate Bill 18 on March 4, 2025, introducing groundbreaking provisions for retroactive child support covering pregnancy-related expenses.
This legislation, sponsored by Senator Merika Coleman (D-Pleasant Grove), allows courts to order child support payments retroactively for the nine months preceding a child’s birth. The bill’s key provisions include:
- Paternity establishment requirement: Retroactive support only applies when paternity is legally established within one year of the child’s birth.
- Live birth limitation: Amendments explicitly restrict retroactive claims to cases involving live births, preventing claims for pregnancies ending in stillbirth.
- Judicial discretion: Unlike previous versions requiring mandatory retroactive support, judges now have discretion to determine whether ordering such support serves the child’s best interests.
- Coverage scope: Support can cover prenatal medical expenses, maternity clothing, and other pregnancy-related costs incurred before birth.
Senator Coleman emphasized that this legislation recognizes financial obligations beginning at conception, aligning with Alabama’s existing personhood laws while providing flexibility for situations where fathers voluntarily supported mothers throughout pregnancy.

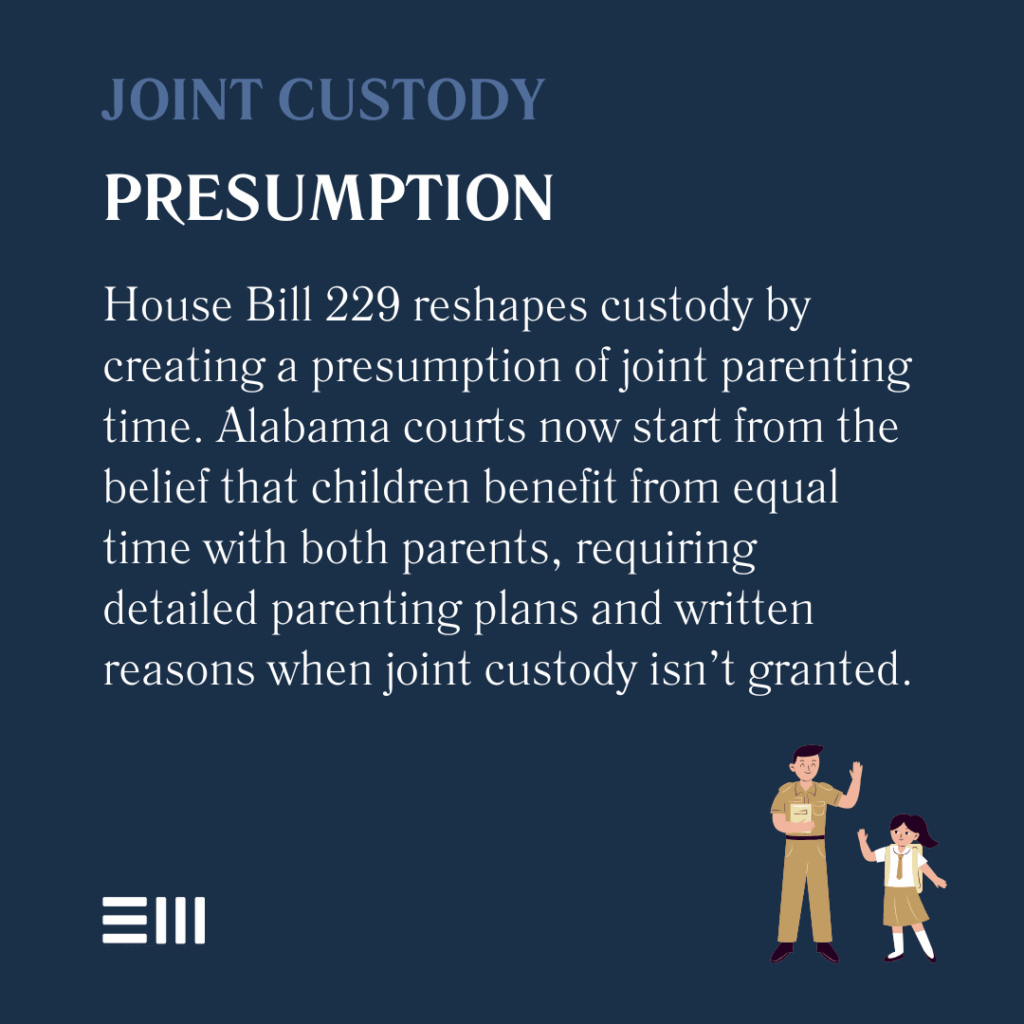
House Bill 229: The Best Interest of the Child Protection Act
Representative Kenneth Paschal (R-Pelham) introduced House Bill 229 on February 15, 2025, proposing the most comprehensive overhaul of Alabama custody laws in nearly two decades.
The legislation establishes a rebuttable presumption favoring joint custody arrangements, fundamentally shifting how Alabama courts approach custody determinations. Major changes under HB 229 include:
- Equal time definition: “Frequent and substantial contact” now means equal or approximately equal time with both parents.
- Mandatory parenting plans: All custody cases require detailed parenting plans, not just those requesting joint custody.
- Written justification requirements: Courts must document specific reasons for deviating from joint custody presumptions.
- Enforcement mechanisms: New remedies include makeup parenting time, reimbursement for costs, and attorney fee awards for schedule violations.
- Expedited relief provisions: Parents believing joint custody endangers their child can file expedited motions, with penalties for bad-faith filings.
The bill addresses concerning statistics showing children with limited parental contact face higher risks of educational failure, substance abuse, and teenage pregnancy, emphasizing the importance of maintaining meaningful relationships with both parents when safe and appropriate.
Modifications Under New Alabama Child Support Laws
Understanding when and how to modify existing support orders remains crucial as new Alabama child support laws take effect.
Alabama courts permit modifications when substantial and continuing material changes in circumstances occur. Common grounds for modification include:
- Income fluctuations: Significant increases or decreases in either parent’s earnings through job loss, promotion, or career changes.
- Childcare expense changes: Alterations in daycare costs, after-school care needs, or elimination of childcare requirements.
- Health insurance modifications: Changes in coverage availability, premium costs, or the party providing insurance.
- Additional children: Birth or adoption of subsequent children affecting the obligor’s financial obligations.
Courts generally apply the 10% variance rule: if recalculated support differs by more than 10% from current obligations, modification is typically warranted.
Importantly, modifications only apply prospectively from the filing date, emphasizing the importance of prompt action when circumstances change.
Enforcement Mechanisms and Compliance
New Alabama child support laws maintain robust enforcement mechanisms to ensure consistent support payments.
The Child Support Enforcement Division employs various tools to secure compliance, including:
- License suspension authority: Driver’s licenses, professional licenses, and recreational licenses can be suspended for non-payment.
- Asset seizure capabilities: Bank accounts, tax refunds, and lottery winnings may be intercepted to satisfy arrears.
- Credit bureau reporting: Delinquent accounts are reported to major credit agencies, affecting credit scores.
- Contempt proceedings: Willful non-payment can result in jail time and additional financial penalties.
The state’s centralized payment system through ACDD ensures accurate record-keeping and transparent accounting of all transactions, protecting both obligors and recipients while maintaining clear payment histories for potential future proceedings.
Impact on Existing Orders
Current child support orders remain valid under new Alabama child support laws, with specific provisions addressing how changes affect existing arrangements.
House Bill 229 explicitly states its provisions will not apply retroactively to existing custody orders when enacted on January 1, 2026. However, parents may petition for modifications based on the new statutory framework if they can demonstrate:
- Material circumstance changes: Significant alterations in living situations, work schedules, or children’s needs.
- Best interest considerations: Evidence that current arrangements no longer serve children’s developmental or emotional needs.
- Compliance history: Documentation of consistent adherence to existing orders when seeking expanded parenting time.
- Geographic feasibility: Practical ability to implement equal or expanded time-sharing based on parents’ locations.
Parents should carefully document any factors supporting modification requests, as courts will scrutinize petitions to ensure changes genuinely benefit children rather than merely accommodating parental preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Alabama Child Support Laws
Understanding new Alabama child support laws requires clarity on how these changes affect everyday situations that families face.
How Will Senate Bill 18 Affect Current Pregnancies?
Senate Bill 18’s retroactive support provisions apply only to support orders established after the law’s effective date.
Expectant mothers should maintain detailed records of pregnancy-related expenses, including medical bills, prenatal vitamins, maternity clothing, and transportation costs for medical appointments.
Courts will consider these documented expenses when determining appropriate retroactive support amounts if paternity is established within the child’s first year.
Does House Bill 229 Guarantee 50/50 Custody?
Despite common misconceptions, HB 229 does not mandate equal time-sharing in all cases. The legislation creates a presumption favoring joint custody that can be rebutted by evidence showing such arrangements would harm the child.
Factors like domestic violence, substance abuse, geographic distance between parents, or a child’s special needs may justify alternative custody arrangements. Alabama judges retain discretion to craft custody orders serving each child’s unique circumstances.
What Constitutes a Material Change for Modification?
Alabama courts recognize various circumstances as material changes justifying support modification.
These include involuntary job loss resulting in 20% or greater income reduction, promotion or career advancement increasing income substantially, children developing special medical or educational needs, relocation affecting parenting time logistics, or changes in childcare requirements as children age.
The key requirement remains that changes must be substantial, continuing, and materially affect either parent’s ability to meet obligations or children’s financial needs.
How Are Self-Employed Parents’ Incomes Calculated?
New Alabama child support laws maintain existing provisions for determining self-employed parents’ income. Courts examine tax returns, profit and loss statements, business bank records, and expense documentation to establish accurate income figures.
Judges may impute income based on earning capacity if they find parents deliberately underreporting earnings.
Self-employed individuals should maintain comprehensive financial records demonstrating legitimate business expenses while accurately reflecting available income for support calculations.
Can Parents Agree to Different Support Amounts?
While Alabama allows parents to negotiate support agreements, courts must approve any deviation from guideline amounts.
Agreements must demonstrate that alternative amounts adequately meet children’s needs and don’t result from coercion or incomplete financial disclosure.
Courts particularly scrutinize agreements providing support below guideline calculations, requiring clear justification that children’s interests remain protected despite reduced payments.
Take Action on New Alabama Child Support Laws
Navigating new Alabama child support laws requires experienced legal guidance to protect your rights and ensure your children’s financial security.
Whether you’re establishing initial support orders, seeking modifications based on changed circumstances, or addressing custody arrangements under proposed legislation, our experienced family law attorneys here at Baxley Maniscalco understand the complexities these new laws introduce.
Contact our office today to schedule a consultation and develop a strategic approach tailored to your family’s unique situation.
Don’t wait for these changes to impact your existing arrangements—proactive legal planning ensures the smoothest possible transition under Alabama’s evolving family law landscape.
Can't find what you're looking for? Search our site below.